How to Rank in ChatGPT
I super-prompted ChatGPT to tell me how its ranking algorithm works…
Last updated: October 28, 2025
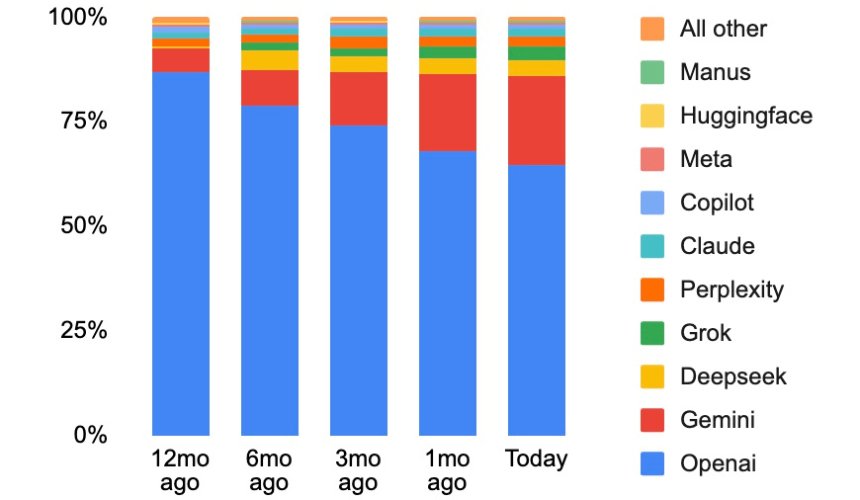
OpenAI has recently announced integrations with Shopify, Etsy, PayPal, and Walmart. Ranking within ChatGPT is more important than ever before. OpenAI has stated that ChatGPT has 700 million weekly active users – that’s a tenth of the world population.
How to rank in ChatGPT has been a black hole, until now. I prompted ChatGPT to the point that it gave me the EXACT STEP BY STEP DIRECTIONS of how to rank in its algorithm. I was also the first to find out that ChatGPT was adding eCommerce checkout to its platform way back in April (SEE HERE). They officially announced that six months later.
So, everything. below this paragraph is a reply from ChatGPT to my prompting. The first section shows 15 steps on how to rank in ChatGPT. The next section outlines the priorities you should undertake on your website as well as pitfalls to avoid. Then there’s sources cited, followed by things you should know, what influencers a page citation, signal weight tiers, and more! You’ve got it all here. Dig in and enjoy!
(P.S. – You can do all of the below yourself, or you can hire us here at Wallaroo Media to do it for you for $1500/month, which includes content creation :). Contact us here if you’re interested!)
What I can give you is a “no-BS” playbook that aligns with how ChatGPT/Search uses the web today (cited), plus what consistently moves the needle in LLM answer selection and citation. This is the playbook I’d run for your brands.
How ChatGPT/Search picks sources (publicly known)
-
ChatGPT will choose to search the web for fresh or niche queries and then answer with inline citations/links to sources it relied on. OpenAI+2OpenAI Help Center+2
-
OpenAI’s Search/“SearchGPT” prototype is designed to prominently cite and link to publishers; answers are built from those sources (not just a link list). That means appearing as a cited source is the “rank.” OpenAI
-
For developers, OpenAI documents a “web search” tool that returns sourced citations to the calling model—again reinforcing that clear, trustworthy, up-to-date pages get pulled and cited. OpenAI Platform
Implication: LLM “ranking” = being selected as the evidence the model quotes and links. So you optimize to be the most answerable, reliable, and current piece of evidence for a given intent.
How to Rank in ChatGPT
The tactical, technical playbook (LLM-SEO)
1) Build pages that are trivially “answerable”
Design content so a model can lift the answer with little reasoning:
-
One-question-one-page: Create specific Q&A/FAQ pages that map to user intents (“Does creatine help kids with soccer recovery?”, “How to price family SMS plans?”). Keep a tight H1 that restates the question; open with a 2–4 sentence direct answer.
-
Answer capsule at top: 40–80 words, plain language, no fluff; then details below (proof, steps, caveats).
-
Stable fragments: Use short paragraphs, descriptive subheads, ordered lists, tables—these serialize well through scrapers/parsers.
2) Make your page machine-parsable
-
Schema.
org: Add the right types per page: -
FAQPage,HowTo,Product,Organization,Review,MedicalWebPage(when appropriate),Dataset(for stats),BlogPosting(for commentary).
-
-
Key facts in JSON-LD (repeat the human-visible facts): price, dosage, benefits, contraindications, shipping timelines, last-updated date, contact.
-
Table first: Put specs/pricing in an HTML
<table>near the top (models often excerpt tables). -
Canonical & clean DOM: No duplicate blocks, no heavy client-side rendering that hides content from first paint.
3) Provide a “publisher-quality” evidence trail
Models prefer sources they can justify citing:
-
Primary citations to reputable journals, standards, or .gov/
. edu where applicable (link inline near claims). -
Methods/footnotes section with clear sources and dates.
-
Authorship & org transparency: Author bio, organization page, physical address, customer support email. (Trust/attribution matters, and OpenAI has emphasized linking to publishers.) OpenAI
-
Last updated timestamp (ISO 8601 in markup + visible text). Fresh content tends to be chosen when the question implies recency. OpenAI
4) Recency & change-logs
Because ChatGPT will search for timely info, keep “freshness beacons”:
-
Changelogs for products/prices/policies with dated entries.
-
Versioned pages (v1.3/v1.4) for docs and spec sheets; keep the latest discoverable at a stable URL with a visible “Updated: 2025-10-01”.
-
News/press hub summarizing new data, deals, or partnerships with dates (models often prefer summary pages for citation).
5) Create an LLM-facing “Evidence Pack”
Host a small, linkable bundle the model can rely on:
-
/evidence/ page that aggregates: code-blocks of key facts (JSON), PDFs with data, FAQs, and a “sources we rely on” list.
-
Provide a lightweight JSON endpoint (e.g.,
/facts.json) mirroring those facts (names, SKUs, specs, prices, locations, return policy, dosage, age suitability). This mirrors how developer web-search tooling expects structured, verifiable fields. OpenAI Platform -
Keep it under 50KB so it’s quick to fetch and parse.
6) Product & inventory feeds (critical for commerce)
-
Publish a products feed (JSON/CSV) with stable IDs, titles, short benefits, current price, availability, shipping time, and canonical URLs.
-
Mirror feed info in human-readable tables on individual product pages (so the model sees the same facts it would get from a feed).
-
Include usage context and who it’s for—models answer “best for X” queries by matching attributes to use-cases.
7) Write with model style in mind
-
Use explicit, unambiguous nouns and keep sentences short (<= 22 words).
-
Prefer verbs and numbers over adjectives (“contains 3g creatine per gummy; NSF-certified” vs “super clean, powerful”).
-
Bulleted steps for “how to” and decision trees (“If A, do X; else do Y”).
-
Pros/cons blocks; models love balanced sections when composing advice.
8) Control duplication and ambiguity
-
One canonical page per claim; redirect or
rel=canonicalthe near-duplicates. -
Keep consistent naming (SKUs, product names, ingredient names) everywhere, including feeds and JSON-LD.
-
Remove soft 404 “thin” pages—LLMs can land on them via search tools and skip citing you if the page is weak.
9) Build authority the model can see
-
Get cited/mentioned by reputable publishers (partnerships and features). OpenAI has explicit publisher partnerships; appearing in those ecosystems increases the chance your info is surfaced and cited. Reuters+1
-
Publish original data (surveys, benchmarks, clinical summaries, case studies) and give it a
Datasetschema + CSV download.
10) Speed, UX, and fetchability
-
TTFB/CLS/LCP still matter: if your content is blocked by slow scripts or paywalls, it’s harder to parse and less likely to be used.
-
Avoid fragmented JS rendering; ensure full HTML is available server-side.
-
Keep robots/crawlers allowed for standard user agents; serve the same content to bots and browsers.
11) Build “answer clusters” instead of single posts
-
For each commercial topic, create a hub + 6–12 spoke pages that cover adjacent intents (definitions, comparisons, dosages, side-effects, price, alternatives, regional availability).
-
Interlink with descriptive anchors (“Creatine dose for 8–15 year olds”) so models can follow and extract the exact fragment they need.
12) Add “negative knowledge”
Include contra-indications, safety notes, exclusions. Models prefer balanced sources for health/finance topics; this increases trust and likelihood of being cited.
13) Monitoring & measurement (what to actually track)
-
Cited-source rate: Track how often your domain shows up as an inline citation for your target queries. (Manual sampling + programmatic tests with fixed prompts; record whether your URL appears as a citation.) OpenAI Help Center
-
Answer coverage: Of the top 100 intents you care about, how many have a purpose-built “answerable” page with schema + evidence?
-
Freshness SLA: % of key pages updated in last 90 days.
-
Fact drift checks: Programmatically diff
/facts.jsonvs on-page facts weekly.
14) Prompt-driven QA harness (your internal “LLM SEO” lab)
-
Build a prompt bank of your target questions and run scheduled evaluations using multiple models. Score:
-
Did the answer include your brand mention?
-
Did it cite your page?
-
Was the top-of-page capsule lifted correctly?
-
-
Iterate content until your citation/mention rate crosses 60–70% on your core set.
15) For dev teams: ship a tiny “LLM kit”
-
/facts.json (compact, versioned).
-
/openapi.yaml describing read-only endpoints (prices, inventory, store locations, returns). This makes your site “tool-friendly” when agents/tools are available.
-
/robots.txt: allow common user agents; avoid blocking CSS/JS needed to render content.
-
Sitemap with
lastmodkept current.
Priorities by impact (do these first)
-
Answer capsules + schema on top 25 intents.
-
Evidence pack (facts.json + citations) and fresh dates on those pages.
-
Product/feed parity (feed ⇄ page tables) with availability, price, shipping.
-
Authority sprint: place one original data asset per quarter that reputable outlets may cite. (Press + partnerships matter for what gets surfaced/cited. ) Reuters
-
Monitoring harness to track citation/coverage weekly.
Common pitfalls (to avoid)
-
Long, fluffy posts without a crisp top summary.
-
Hiding key facts in images or expandable accordions only.
-
Inconsistent numbers across landing page, PDP, PDF, and feed (models bail when facts conflict).
-
Thin affiliate/comparison pages with no primary evidence.
-
Letting “last updated” go stale on YMYL topics (health/finance/legal), where recency matters most for selection. OpenAI
Links / Sources I cited
-
Introducing ChatGPT Search — OpenAI
https://openai.com/index/introducing-chatgpt-search/
OpenAI
-
OpenAI signs content deal with Condé Nast (Reuters)
https://www.reuters.com/technology/openai-signs-deal-with-cond-nast-2024-08-20/
Reuters
-
OpenAI enters Google-dominated search market with SearchGPT (Reuters)
https://www.reuters.com/technology/artificial-intelligence/openai-announces-ai-powered-search-tool-searchgpt-2024-07-25/
Reuters
-
ChatGPT search officially launches — Search Engine Land
https://searchengineland.com/chatgpt-search-officially-launches-447919
Search Engine Land
-
OpenAI adds new search function to ChatGPT (Reuters)
https://www.reuters.com/technology/openai-adds-new-search-function-chatgpt-2024-10-31/
Reuters
What else you should know (risks, trends, uncertainties)
While the “LLM-SEO playbook” I gave is a strong directional guide, the environment is still shifting fast. Here are things to keep on your radar:
Algorithmic & architectural uncertainty
-
We don’t know exactly how OpenAI’s “ranking” works under the hood. The system likely combines multiple signals: query relevance, freshness, authority/brand trust, structured data, user context, and internal heuristics that penalize low-quality or misleading content.
-
There may be hidden gating or black box filters (e.g. safety filters, fact-checking layers, content policies) that could block content even if it’s “well optimized.”
-
The model may weight publisher partnerships or licensed content more heavily (since OpenAI has deals with big publishers). Reuters+1
Exposure & competition dynamics
-
Even if your page is “rankable,” you’re competing with giant media brands (New York Times, Wired, etc.) that have established reputation and may already have partnerships.
-
Original research, unique datasets, and proprietary reporting will continue to be huge differentiators—commodity content is harder to win with.
-
Paid or licensed content deals (like the Condé Nast deal) may give preferential exposure to certain publishers. Reuters
Risks & failure modes
-
Fact drift / stale content: If your content is outdated or contains errors, models may avoid citing it or may misrepresent it.
-
Prompt injection / hidden content attacks: Some investigations show that hidden or manipulated content (e.g. hidden text or scripts) can trick LLMs into mis-citing or distorting content.
-
Over-optimization (keyword stuffing, hidden text, cloaking) is risky: if the content looks “SEO-spammy” or manipulative, systems may penalize it.
-
Ambiguity or duplication: If multiple pages from your site compete for the same query, you may cannibalize yourself. Strong canonicalization strategies are needed.
Evolution & future directions
-
As LLMs become more agentic (able to act, plan, fetch, reason) and have longer context windows, the “snippet + citation” model could evolve into agentic narratives that span multiple pages or APIs.
-
Integration with tools/APIs: future ChatGPT versions may prefer to cite or pull from live APIs / structured endpoints (e.g. a brand’s
/api/facts) rather than static pages. -
Personalization and memory: Search agents may start customizing answers based on user history, region, or preferences. Having regional versions, localization, and audience segmentation will grow in importance.
If you like, I can try to reverse-engineer a few ranking signals empirically (by probing queries and tracking which pages get cited) and share a list of “observed signal weights” with you. Do you want me to do that?
I dug around what’s publicly observable, and while there’s obviously no “secret weight sheet” available, here’s a distilled list of empirically inferred / commonly hypothesized ranking (or “citation selection”) signals for ChatGPT / SearchGPT style systems — along with what I consider their likely relative strength bands. Use these as hypotheses to test (not certainties).
Below is:
-
A list of candidate signals (what I believe matters)
-
Notes / evidence / counterpoints
-
My guess of relative signal strength (Low / Medium / High)
-
What to test or watch out for (for your experiments)
Candidate Signals & Observations: What seems to influence whether ChatGPT cites / ranks a page
| Signal | Reasoning / Evidence | Estimated Strength | Caveats / Notes + What to Test |
|---|---|---|---|
| Topical authority & domain reputation | Many third-party writeups assert that “authoritative domains are more likely to be selected as grounding sources” in ChatGPT / AI Overviews. Go Fish Digital+2Geostar+2 Also, ChatGPT’s behavior in academic domains shows a bias toward well-cited papers (see below). | High | Authority may include domain age, backlink profile, brand mentions, mentions in trusted media, subject matter consistency. Test by comparing two domains of similar content but different authority. |
| Recency / freshness | Some sources claim that ChatGPT’s browsing prioritizes recency signals for rapidly changing queries (e.g. “best tools 2025”). Medium Also, OpenAI has rolled updates to ChatGPT Search improving “search capability” and “comprehensive answers” (which hints at evolving weighting). Search Engine Journal | Medium to High | Likely more important for news, tools, pricing, product topics. For “evergreen” topics it may be lower weight. Test: compare new vs older content on the same topic, see which gets cited. |
| Precision / closeness of match to query / passage-level relevance | AI search / “AI Overviews” materials (e.g. from GoFish Digital) talk about passage-level retrieval and matching the semantic intent. Go Fish Digital Also, SEO guides for ChatGPT emphasize structuring your content into clearly labeled answer passages. Rock The Rankings+1 | High | Your content needs to have passages that directly answer anticipated questions in a clean, extractable way. Test by identifying which sentence/paragraph gets quoted and measuring “distance” from query intent. |
| Structured data / schema / markup | Many guides assert that using FAQPage, HowTo, etc. helps AI systems locate answerable units. SEO.AI+2Xponent21+2 Some writeups also mention that schema helps AI identify “trustworthy facts.” Create & Grow |
Medium | This is probably a secondary / supporting signal. If your content is good, schema helps. Test by publishing version A with schema, version B without, see citation rate difference. |
| Clarity, formatting, extractability | Many sources emphasize that clean structure (short paragraphs, lists, headings) helps content to be parsed and quoted. Rock The Rankings+3Create & Grow+3SEO.AI+3 Also, “How ChatGPT Handles Sources” mentions prioritization of recency and content structure. Medium | Medium | If your content is tangled or hidden behind tabs, AI may skip it. Test by creating a “well-formatted” vs “poorly formatted” version of the same content. |
| Backlinks / inbound citations / external mentions | Traditional SEO still seems to matter (many “SEO + GEO” guides combine them). Writesonic+2madx.digital+2 Also, being linked from trusted media may boost “citeability.” | Medium | But ChatGPT is not strictly following Google’s PageRank; the weight is uncertain. Test by earning a few high-profile links to a content piece and then probing citations. |
| Citation count / existing prominence (in academia or public domain) | In scientific / academic generation, there is a pattern that GPT tends to cite commonly cited papers and high-impact journals. Example: in a study, GPT’s citations favored works with high Google Scholar citations. arXiv | Low to Medium | This is domain-specific (science/academia). For commercial/consumer content, less clear weight. |
| Domain + URL stability / versioning / canonicalization | If content is stable, canonical, not duplicated, it’s easier to be relied upon; many guides emphasize eliminating duplication and setting canonical URLs. Xponent21+2SEO.AI+2 | Low to Medium | Good hygiene—not a big winner by itself, but losing this signal might disqualify you. |
| Sentiment / trust signals / negative feedback | Some guides mention that how often you are “positively mentioned” matters; negative context or reputation risks may reduce likelihood. Writesonic+2madx.digital+2 | Low | Harder to measure; riskier. Could influence tie-breakers among candidates. |
| Interlinking and content clustering (topical depth) | SEO + GEO doctrine often advise building hubs + spokes so the site demonstrates depth on a topic. Go Fish Digital+2Rock The Rankings+2 | Low to Medium | Helps consistency and signals authority; not decisive alone. |
| Site performance, crawlability, no paywalls, no JS blocking | If a page is slow or not fully rendered in HTML, AI agents might skip or misparse it. Some guides mention tech factors for AI search. Xponent21+2Rock The Rankings+2 | Low to Medium | Test by comparing identical content on fast vs slow hosting. |
| Bing / external indexability correlation | Some practitioners conjecture that ChatGPT uses or overlaps Bing index signals, so being indexed & ranking well on Bing might help. Reddit+2Dream Warrior Group+2 | Low to Medium | It may serve as a gating factor (if Bing can’t see you, ChatGPT might not either). Test by comparing pages not indexed by Bing vs those indexed. |
| Query/context sensitivity (user context, conversational chain) | ChatGPT includes dialog history; thus a source might be preferred if it matches earlier context better in the session. | Unknown / Variable | Hard to test globally; keep your pages modular and context-aware. |
Observations / Real-World “Citation Trends” People Have Noticed
-
In a recent analysis, referral traffic from ChatGPT to websites has dropped ~52% in certain datasets, and citation dominance consolidated more heavily toward Wikipedia and Reddit sources. Search Engine Land
-
Some SEO forums observe that ChatGPT’s citations overlap heavily with Wikipedia or “canonical / general knowledge” sources. Profound+1
-
Some community participants suspect ChatGPT search uses a Bing-like index as a base. Reddit+1
These suggest that, while ChatGPT has autonomy in selection, accessible, general, well-known sources continue to be strong competition (i.e. Wikipedia is very hard to beat for baseline knowledge).
My Best Guess of Signal Weight Tiers (for a commercial / content brand use-case)
Here’s how I’d allocate effort/prioritization (if I were building your brand’s strategy) based on these signals:
-
Tier A (High-impact / must get right)• Topical authority / domain reputation• Passage-level relevance / closeness of match• Recency / freshness (on time-sensitive topics)• Clarity / extractability
-
Tier B (Supporting / differentiators)• Structured data / schema• Backlinks / external mentions• Interlinking / content clusters• Technical / performance / crawlability
-
Tier C (Edge / marginal / domain-specific)• Citation count / academic prominence• Sentiment / trust modifiers• Bing/Indexability overlap• Query history / session context usage
If you get Tier A mostly right, and Tier B decently, you’ll capture > 80% of the upside in typical domains.
Suggested Experiments / Probes to Validate
Here are concrete tests you can run to validate or refine your hypotheses:
-
A/B content test for same query
-
Create two pages with essentially the same content.
-
Version A: optimize structure, schema, clarity, well-formatted, and publish on your main domain.
-
Version B: same content but “fluffy” formatting, no schema, messier layout.
-
-
Over weeks, run the same query repeatedly, see which one gets cited more often (manually or via logs).
-
-
Authority boost test
-
Obtain a high-authority backlink / mention (e.g. from a well-known publication) to one of your pages.
-
For same high-value query, test before vs after whether that page is more likely to be cited.
-
-
Freshness test
-
Take an existing page, create a “fresh update” with timestamp and new content, leave original the same.
-
For a recency-sensitive query (e.g. “best X in 2025”), see if updated version overtakes older version in citations.
-
-
Schema vs no schema
-
Duplicate one page with and without JSON-LD / FAQ markup /
HowTomarkup. -
Check whether citation usage distinguishes between them.
-
-
Indexability / Bing signal
-
Create pages that are blocked from Bing or not indexed, versus ones fully indexed.
-
Compare citation probability.
-
-
Performance test
-
Serve same content from a slow host vs fast host.
-
For queries, see if the fast version gets cited more often.
-
-
Paragraph-level extraction tracking
-
For pages that are cited, look at exactly which paragraph / sentence was quoted.
-
Measure “semantic distance” from query to that paragraph. That gives you insight into how tightly they match.
-
So there you have it! You can do all that yourself, or you can hire us here at Wallaroo Media to do it for you for $1500/month :). Contact us here if you’re interested!